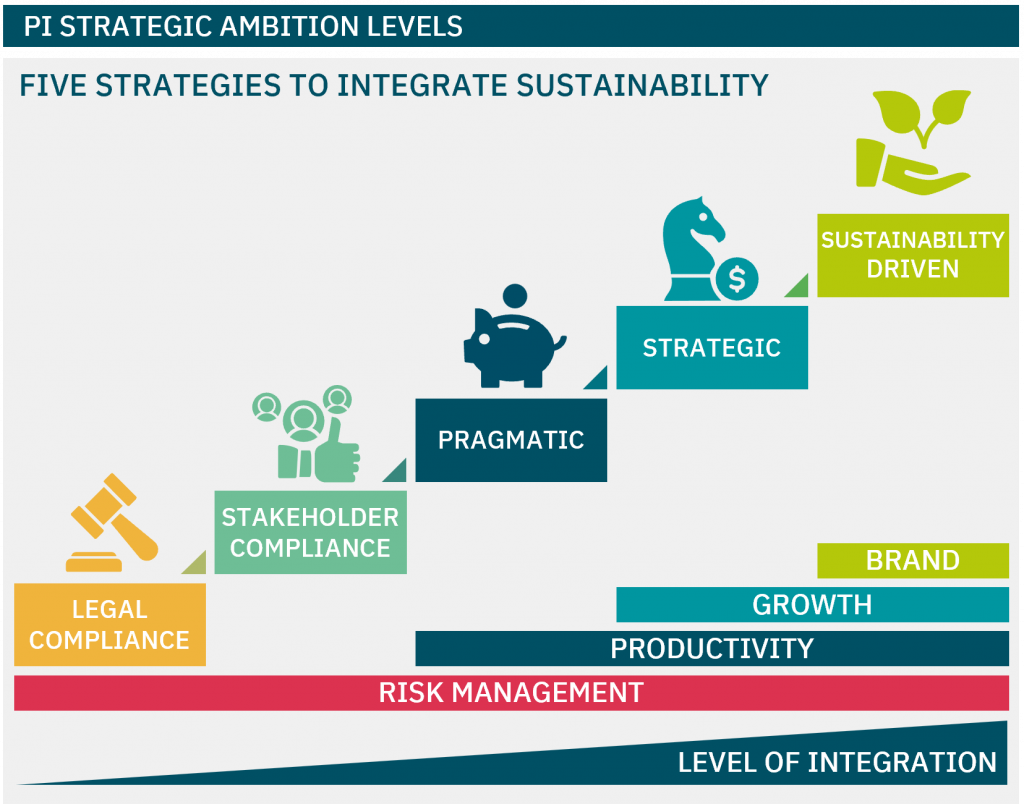
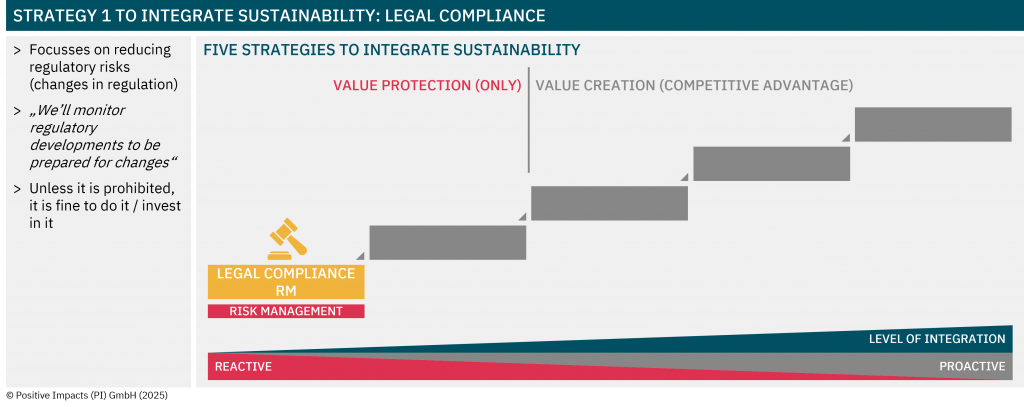
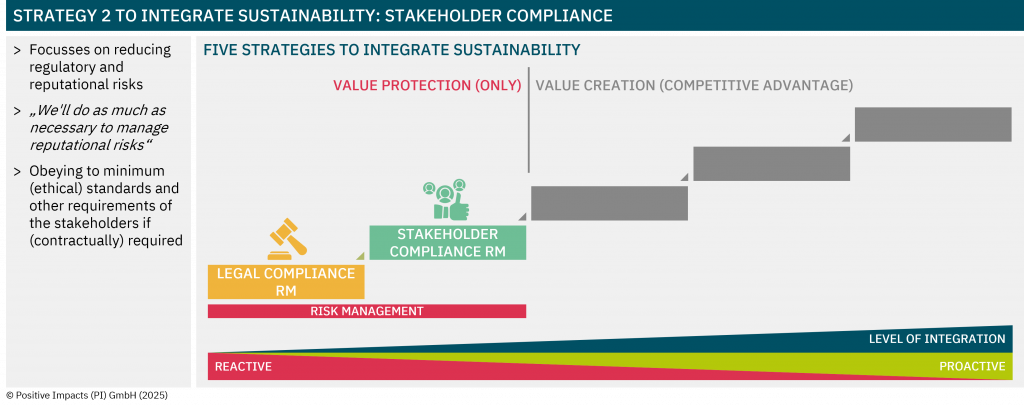
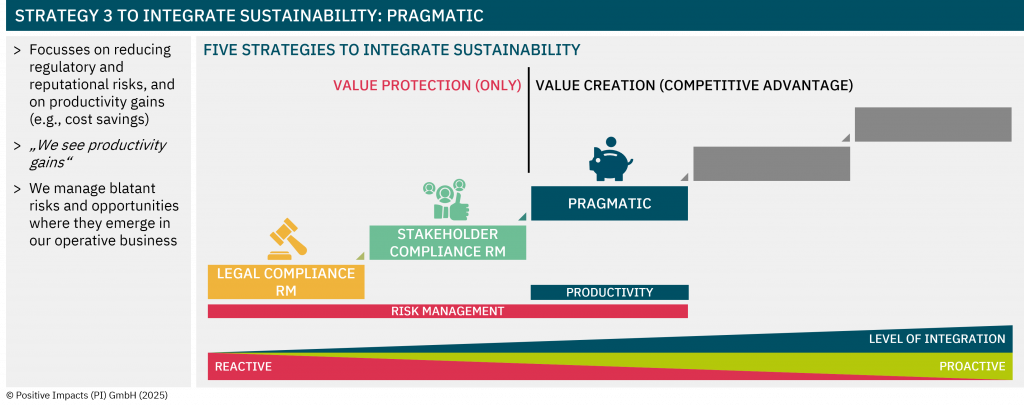
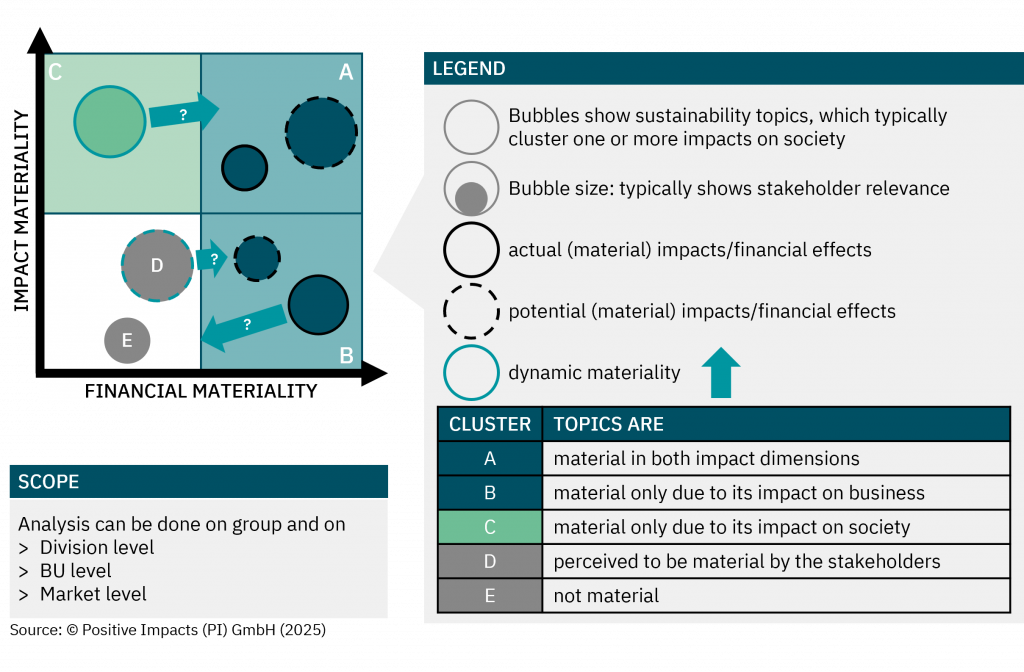
Embedding Sustainability into Core Strategy
for organizations
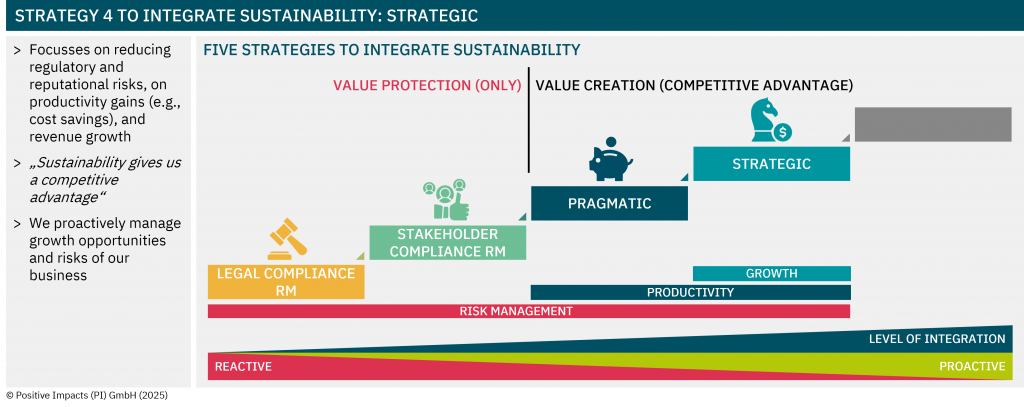
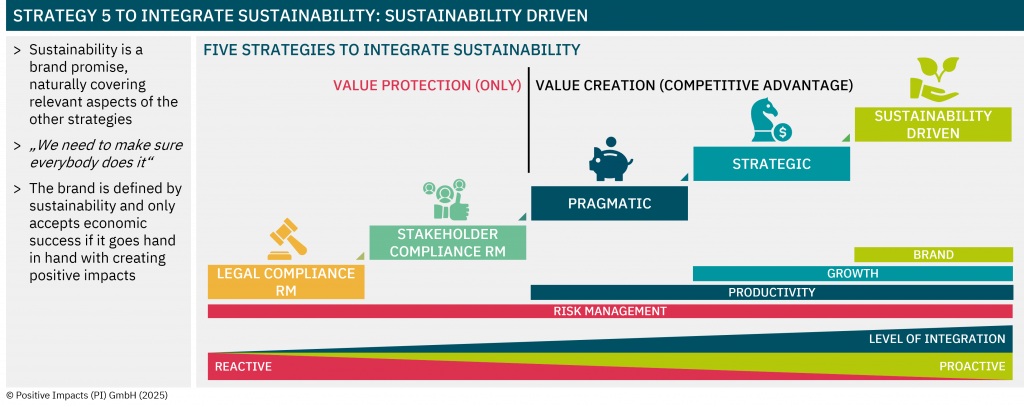
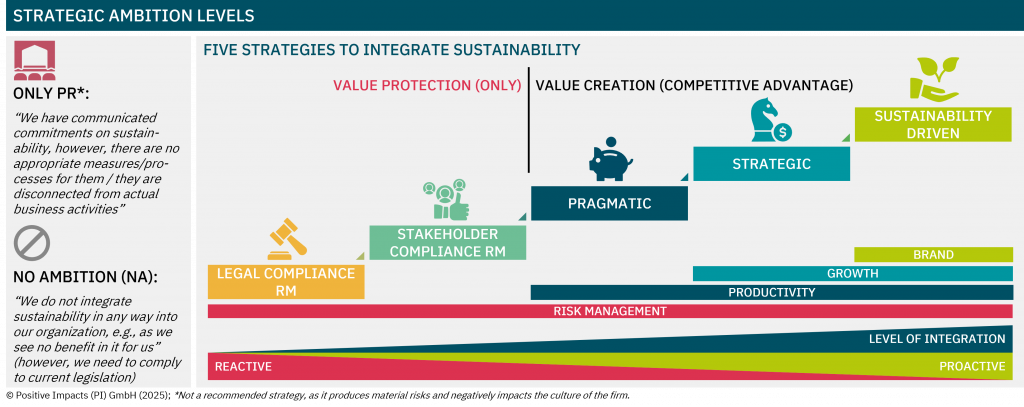
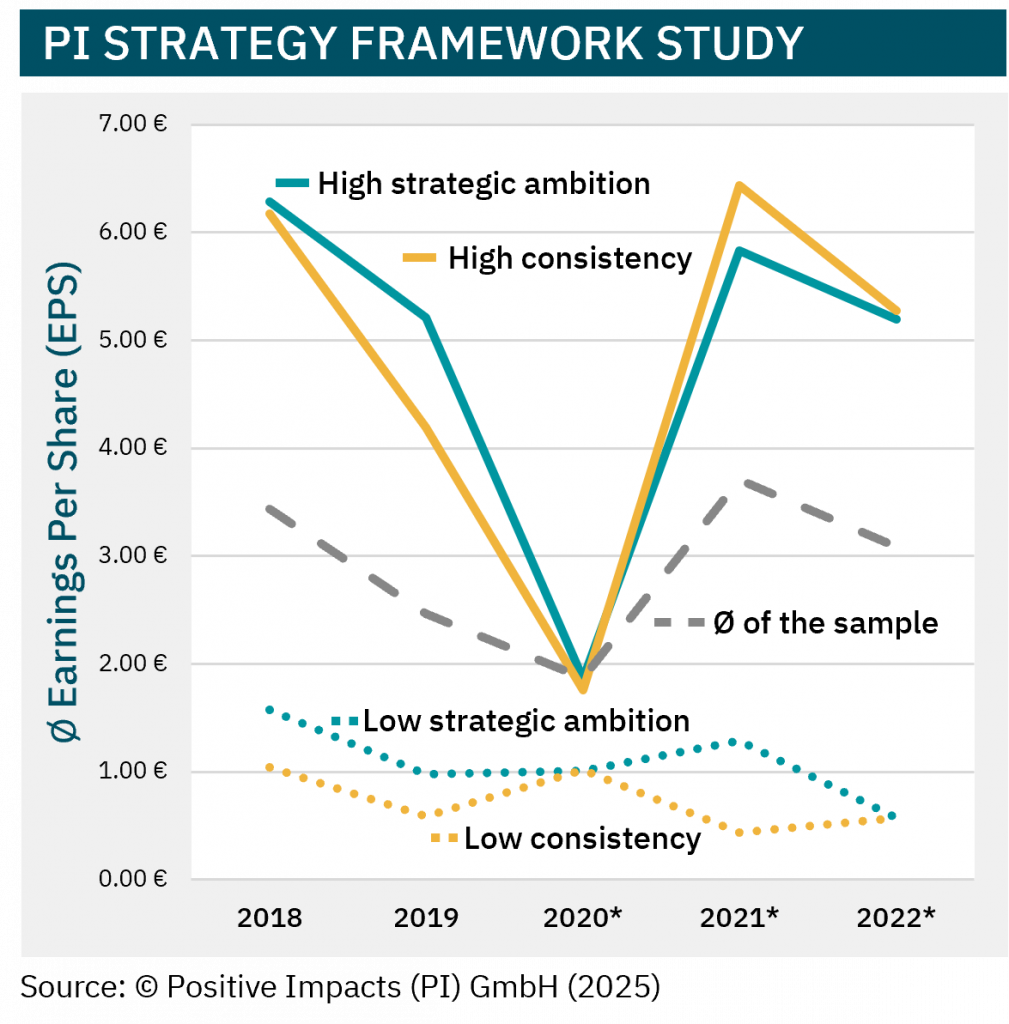
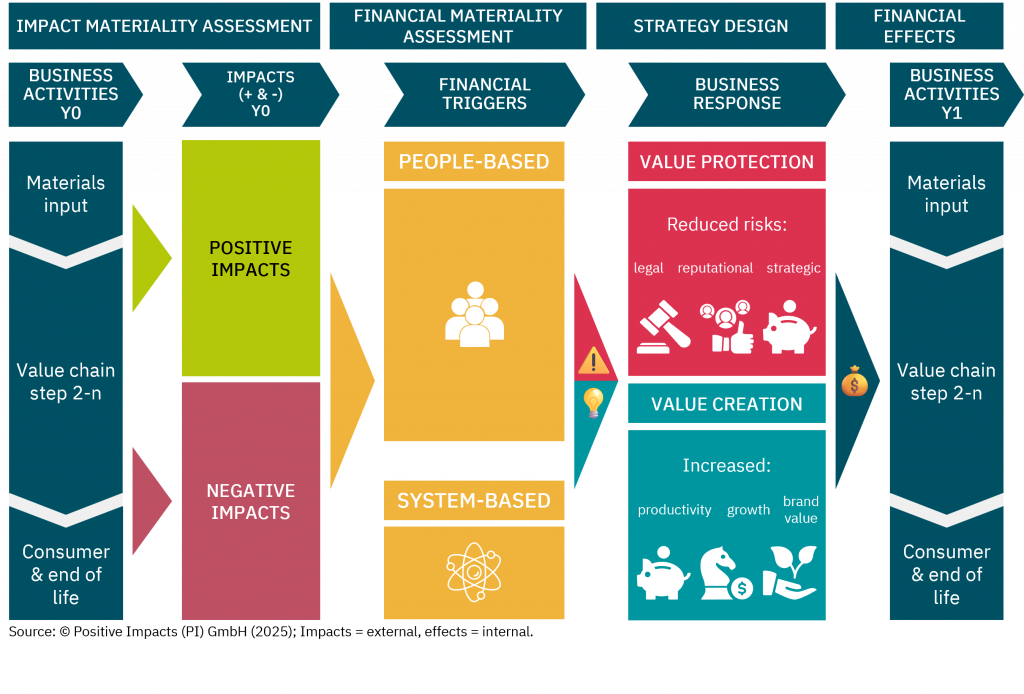
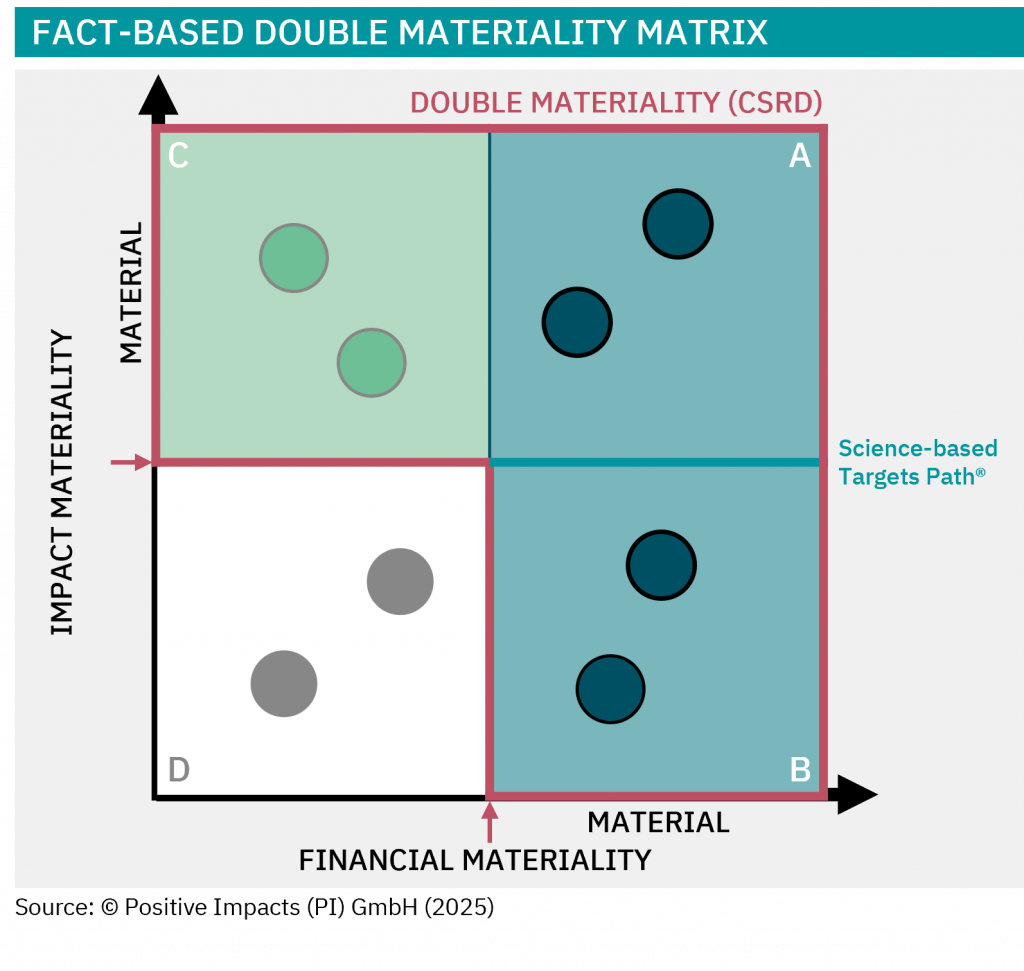
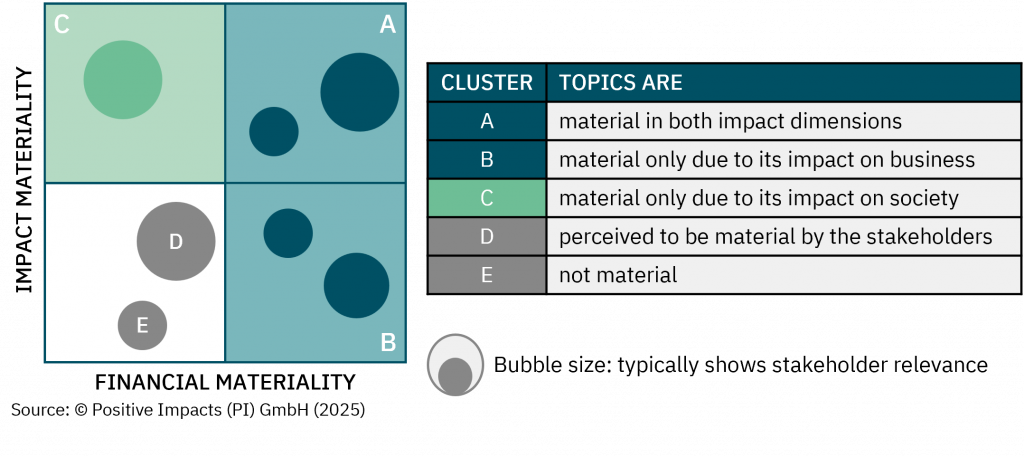
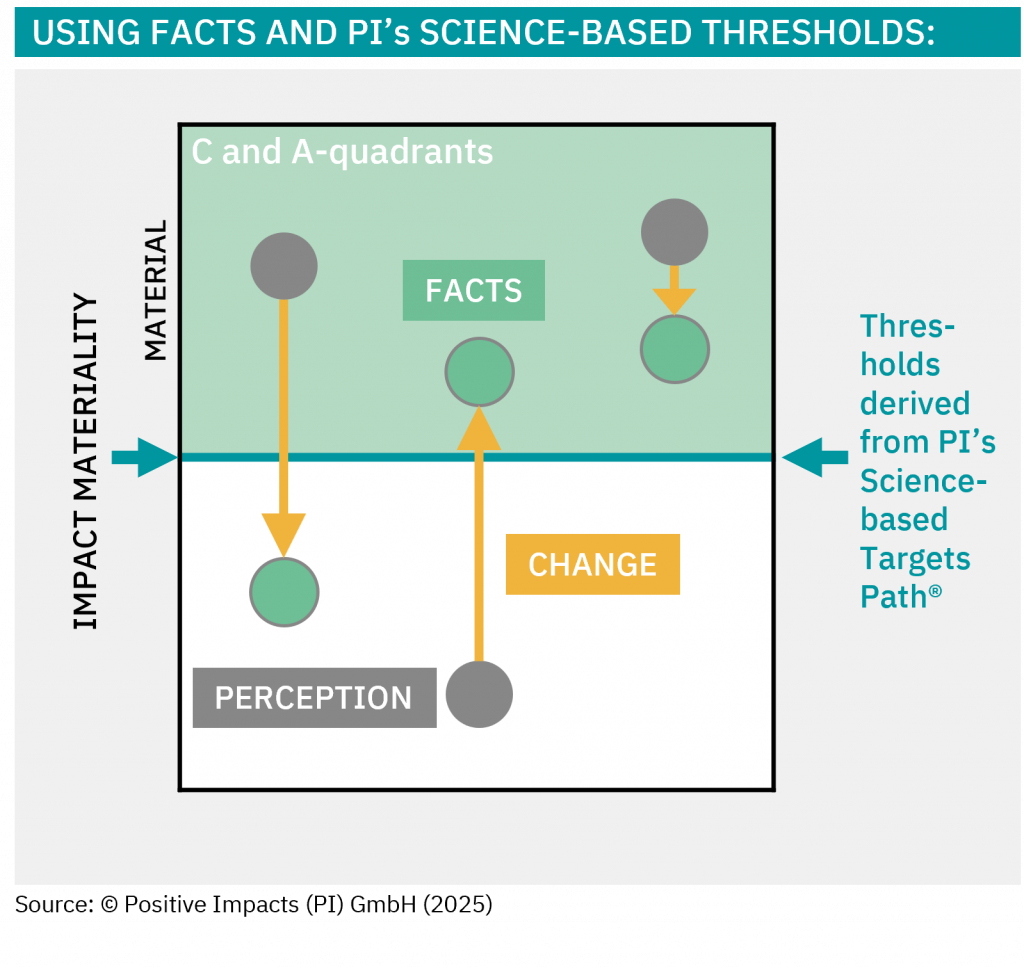
Discover the degree to which sustainability is embedded in your strategy, what that means for your impact, risk, and long-term value, and how to embed sustainability into your core business strategy.